Recently, Linux kernel 5.7 was released with plenty of bells and whistles, which further improves Linux OS capabilities. In this article, we will go through the process of installing Linux kernel 5.7 on Ubuntu. However, before we go forward, let's learn about Linux Kernel briefly.
What is the Linux Kernel?
Linux kernel is a monolithic, open-source, and free operating system kernel based on Unix. Linux kernel is versatile when it comes to computing systems as it supports mobile devices, tablets, computers, mainframes, supercomputers, smartwatches, and so on.
Linus Torvalds first created the first version of the Linux kernel (0.01) in 1991. He created it for his personal computer with no intention of making it cross-platform. Soon, it became popular, which resulted in him and the open-source community working on the Kernel and improving it in the coming years. To ensure fair usage and distribution, it adopted the GNU Operating System License, which made it popular among both users and developers.
How does Kernel Release Work?
Kernel development is mainly the contributors work worldwide. The Linux Kernel discussions are done through the Linux kernel mailing list (LKML). The stable release model was adapted in 2005, which was done to improve the feedback and improvement cycle. Initially, it was done in 2-3 months, which meant that longer feedback and implementation cycle, resulting in both developer's and user's frustration.
To improve the whole scenario, the releases are cut down to one week, depending on other factors, including holidays, workload, and so on. The numbering in these kernel release is done like 5.6.1, 5.6.2, 5.6.3, and so on. The big releases are done by using the notion of two numbers, for example, 4.9.
The latest big kernel release is the 5.7. We also have LTS kernels, which come with long-term support for better wide-adoption. Apart from releases, there are patches. The patches follow different ruleset and are used to improve the quality of the Kernel as more and more users and developers play with it.
There are, of course, patch rules as well to ensure the Kernel's stability. The patch rules have seen no change in the past 12 years and hence provided stability and effectiveness.
To ensure that a kernel change is stable, it needs to meet the following:
- The change should not be more than 100 lines
- It should be adequately tested and corrected.
- The fix should be only one thing at one time.
- The fix should only be provided on a reported issue.
- No significant functionality is released in patches.
- It should be merged into Linux trees
Linus Torvalds is responsible for reviewing and releasing the patches or significant releases.
If you are still curious, then you should read the Linux Kernel Release Model.
Why a need for Kernel release?
Kernel releases are vital for the survivability of any operating system. Not only they bring new features, but they also ensure proper stability and security for the user.
For example, The Linux kernel marks security bugs as high priority and patches and push them out as soon as possible. There are many guidelines on how to ensure kernel security, which is beyond the scope of the article.
Kernel 5.7 Features
With a good understanding of Kernel, Linux Kernel release model, and the need for it, let's briefly list the Kernel 5.7 features below.
- New hardware support with exFAT driver
- Extended ARM devices support
- Zstd compression support
- Task scheduler thermal pressure checking
- IO_uring improvements
and many more! If you are interested in learning more, then you can check out our complete coverage here.
How to install Linux Kernel 5.7 on Ubuntu
In this section, we will learn how to install Linux kernel 5.7 on Ubuntu. This method will also work for any Debian-based distro.
Let's get started.
At first, you need to download all the required files using wget. To do so, simply copy and paste the following commands in the terminal.
You might want to change to /tmp/ folder using the command below.
cd /tmp/
wget https://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v5.7/linux-headers-5.7.0-050700_5.7.0-050700.202005312130_all.deb
wget https://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v5.7/linux-headers-5.7.0-050700-generic_5.7.0-050700.202005312130_amd64.deb
wget https://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v5.7/linux-image-unsigned-5.7.0-050700-generic_5.7.0-050700.202005312130_amd64.deb
wget https://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v5.7/linux-modules-5.7.0-050700-generic_5.7.0-050700.202005312130_amd64.deb
Now, all the files are downloaded, you should run the following command to install it.
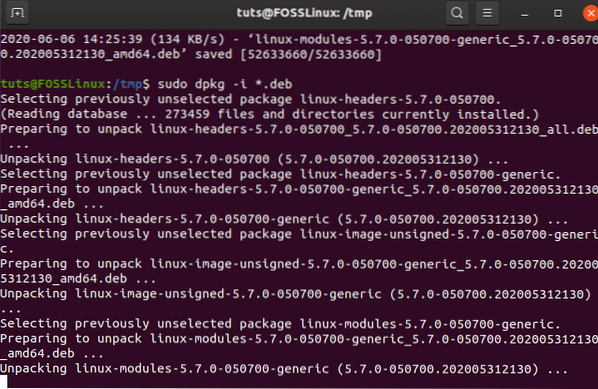
sudo dpkg -i .deb
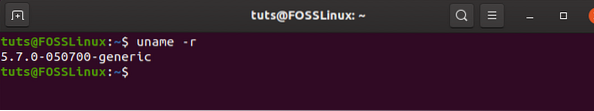
Finally, you need to verify the installation is done or not, run the following command after a system reboot.
uname -r
How to boot to previous Kernels using the grub
To display the GRUB during the booting time, you need to press and hold the SHIFT button. Now, you will see the available kernel options which you can select according to your choice using the up and down arrow keys. Once picked, press ENTER, and you will be booted into Linux using the chosen Kernel. It's that easy!
You can also set the default kernel by editing the grub.
gksudo gedit /etc/default/grub Uninstallation
If for some reason, you want to uninstall kernel 5.7 and revert to the last stable Kernel, then you can do it by running the following command.
sudo dpkg --purge linux-image-unsigned-5.7.0-050700-generic
Conclusion
This leads us to the end of our article on how to install Linux Kernel 5.7 on Ubuntu. So, what do you think about the new Kernel? Did you like it? Comment below and let us know.
 Phenquestions
Phenquestions



